What Are Multi-Chain Stablecoins?
Multi-Chain stablecoins are digital tokens that keep a fixed value across several blockchains. Unlike single-network coins, a multi-chain stablecoin works on different chains at once. It uses smart bridges to wrap and unwrap value, cutting wait times and fees. By sharing liquidity pools on each chain, it boosts funds availability without relying heavily on one bridge. This design eases token flows, reduces risks from a single network, and lets apps move value freely. As a multi-network stablecoin, it connects various chains smoothly, giving users uniform balances. Developers can build services that tap liquidity from all chains at once, instantly reliably.
Current types of stablecoin include fiat-backed, crypto-backed, and algorithmic models. Traditional coins lock assets on one chain, forcing users to swap or bridge tokens. A blockchain-agnostic stablecoin avoids this by minting matching tokens on each network, boosting speed and cutting costs. This approach reduces bridge dependency and lowers risk from one chain failure. As a multi-network stablecoin, this system taps liquidity pools on all chains, giving DeFi platforms more trading depth and flexibility. Regulators look at stablecoin regulation, focusing on proof of reserves. Multi-chain stablecoin systems must follow rules, ensure clear reserve records, and meet compliance checks to stay legal.
Interoperability and Cross-Network Liquidity of Multi-Chain Stablecoins
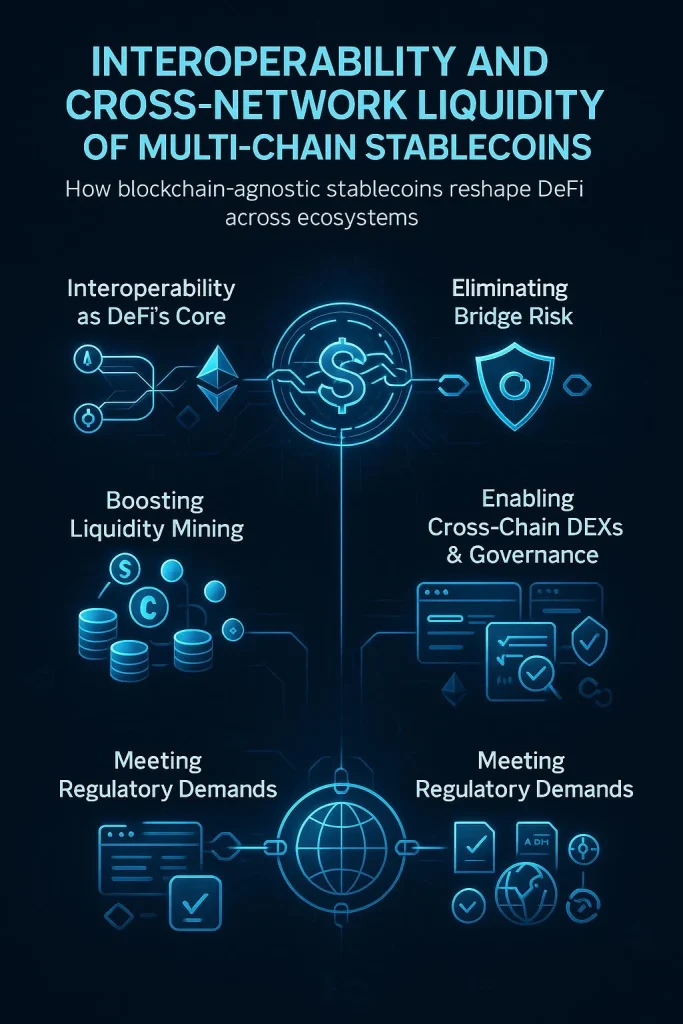
1. Interoperability as DeFi’s Core
2. Eliminating Bridge Risk
3. Boosting Liquidity Mining
4. Enabling Cross‑Chain DEXs & Governance
5. Meeting Regulatory Demands
Decentralized Stablecoin Development: Use Cases and Architecture
1. Architecture Overview
2. Collateral Models
3. Oracle Integration
4. Mint/Burn Mechanics
5. Real‑World Use Cases
How to Build Multi-Chain Stablecoins: Tools, Costs, and Compliance
1. Smart Contract Frameworks
2. Bridge Mechanisms
A multi-network stablecoin uses decentralized bridges and relayers to sync tokens across chains. When users lock collateral on Chain A, bridge oracles emit an event, triggering mint functions on Chain B. Trusted relayer nodes watch these events and authorize token issuance without central custody. This cross‑chain stablecoin design removes single‑point failure risks and limits exposure to compromised bridges. Using modular bridge adapters, developers keep token amounts the same on every chain by syncing transactions and supply between networks in real time. As a multi-chain stablecoin solution, this setup provides instant liquidity transfers with minimal fees and predictable performance.
3. Consensus Requirements
4. Development Costs & Hiring
5. Compliance & Regulation
6. Toolchain & Deployment
Future of Multi-Chain Stablecoins

1. Leading Stablecoins and Their Multi‑Chain Footprint
2. Emerging Blockchain‑Agnostic Projects
3. Real‑World Asset Backing Trends
4. Parallel Multi‑Network Issuance
5. AI, Governance and Future Predictions
Conclusion
Multi-chain stablecoin ecosystems bridge network gaps, enabling seamless value flow and robust liquidity across chains. As a blockchain-agnostic stablecoin solution, they power scalable finance, support diverse DeFi applications, reduce friction in cross-border transactions, and foster truly permissionless markets.
Shamla Tech is a stablecoin development company that builds multi-chain stablecoins for businesses worldwide. We design, audit, and deploy secure cross-chain contracts, integrate bridges and oracles, meeting compliance standards. Our solutions enable fast mint/burn cycles and scalable liquidity, empowering clients to launch resilient blockchain-agnostic stablecoin products backed by transparent reserves.
Ready to launch your own multi-chain stablecoin?
Get in touch with Shamla Tech to build secure, scalable, and compliant stablecoin solutions today!