Any team building a real-world asset tokenization platform runs into the same technical wall early on. Tokens transfer instantly, but regulated assets do not. Investor eligibility, jurisdiction limits, transfer approvals, and administrative actions must be enforced every time ownership changes. For builders, this raises a practical question: can these rules live inside the token itself, or must they stay off-chain?
Most Ethereum token standards were designed for open markets. They assume unrestricted transfers and anonymous holders. That design creates friction when platforms attempt Real World Asset Tokenization, where identity checks and legal controls are mandatory and continuous.
This article explains the ERC-3643 Token, a blockchain standard for Real-World Assets created to support regulated issuance and controlled transfers. We outline how the standard works, how it differs from earlier approaches, and how it fits into production-grade RWA tokenization platforms.
Launch a compliant RWA tokenization platform using ERC-3643
ERC-3643: A Standard for Real-World Asset Tokenization
Real-world asset tokenization converts legally issued assets into on-chain instruments that must follow the same rules as their off-chain form. The ERC-3643 Token specifies how those rules are enforced during issuance, holding, and transfer of tokenized assets.
It defines a contract-level structure for linking tokens to verified investors, applying transfer conditions, and enabling issuer supervision. Built on concepts introduced by the T-REX Token Standard, ERC-3643 is used as a Real-World Asset Token Standard in platforms that tokenize regulated assets such as securities, funds, and structured products.
How ERC-3643 maps to RWA tokenization workflows:
- Legal issuance alignment: Tokens are minted only to wallets associated with approved investor identities defined during offering setup.
- Custody-aware ownership: Token balances represent legally recognized ownership, suitable for self-custody or regulated custodians.
- Rule-enforced secondary markets: Transfers execute only when buyer, seller, and jurisdiction conditions match asset restrictions.
- Issuer and regulator actions: Smart contracts support freezes, forced transfers, and redemptions required by legal or regulatory events.
- Ongoing compliance maintenance: Compliance rules can be updated to reflect regulatory changes without reissuing tokens or migrating holders.
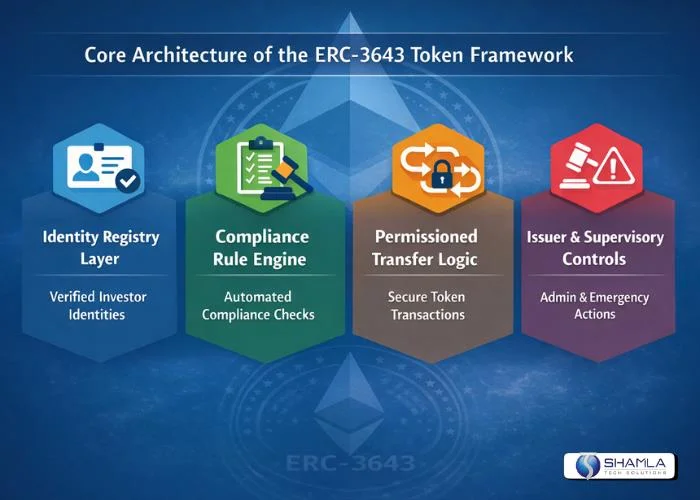
1. Identity Registry Layer
In RWA tokenization, ownership is tied to verified investors, not anonymous wallets. The identity registry in the ERC-3643 Token framework links each holding address to a validated identity record. This allows the platform to represent legal ownership on-chain while supporting different investor types such as individuals, institutions, or custodians.
For RWA tokenization platforms, this layer enables issuer-controlled onboarding, jurisdiction tagging, and revocation of access without touching token balances, aligning on-chain state with off-chain legal records.
2. Compliance Rule Engine
The compliance engine defines the conditions under which a tokenized real-world asset can be issued or transferred. It evaluates factors such as investor eligibility, jurisdiction constraints, and asset-specific restrictions before any state change occurs.
As part of the ERC-3643 Compliance Token Standard, this logic executes directly within smart contracts, ensuring compliance is enforced at settlement time. For RWA tokenization platforms, this removes reliance on manual approvals or off-chain enforcement layers.
3. Permissioned Transfer Logic
Token transfers in RWA systems must reflect how assets trade in regulated markets. ERC-3643 introduces permissioned transfer logic where every transaction is checked against identity and compliance rules before execution.
This makes the standard suitable as a Security Token Standard for RWAs, supporting restricted secondary markets, private placements, and controlled liquidity venues. Builders can integrate trading modules while maintaining confidence that unauthorized transfers cannot occur at the protocol level.
4. Issuer and Supervisory Controls
Real-world assets remain subject to issuer obligations, legal actions, and regulatory oversight after issuance. ERC-3643 includes administrative functions that allow authorized parties to freeze tokens, force transfers, or execute redemptions when required.
In RWA tokenization, these controls support events such as court orders, corporate actions, or compliance breaches. This architecture allows platforms to operate continuously while responding to real-world legal and regulatory requirements.
ERC-3643 vs ERC-1400: Understanding the Difference
ERC-1400 was introduced as an early attempt to standardize security tokens on Ethereum by grouping multiple extensions for partitions, documents, and transfer rules. While it provided a starting point for tokenized securities, many RWA platforms found it difficult to implement in production due to fragmented compliance logic and heavy reliance on off-chain processes.
The ERC-3643 Token takes a different approach by treating compliance as a core protocol function rather than an optional extension. This design makes regulated asset tokenization ERC-3643 more suitable for platforms that must enforce investor eligibility, jurisdiction rules, and supervisory actions continuously across the asset lifecycle.
RWA Requirement | ERC-1400 | ERC-3643 |
Investor eligibility | Checked through external modules | Enforced on-chain through identity linkage |
Transfer restrictions | Managed via partitions and hooks | Validated by a central compliance engine |
Jurisdiction control | Handled off-chain or manually | Evaluated at transfer execution |
Issuer intervention | Limited and inconsistent | Built-in support for freezes and forced transfers |
Long-term RWA operations | Complex to maintain | Designed for ongoing regulatory supervision |
Building Compliant RWA Tokenization Platforms Using ERC-3643
1. Issuance Aligned With Legal Structuring
A compliant RWA platform starts before any token is minted. ERC-3643 allows issuers to encode offering rules defined during legal structuring directly into smart contracts. Investor eligibility, jurisdiction limits, and asset-specific constraints are enforced at issuance time, preventing misallocation from the start.
This approach is central to ERC-3643 Real-World Asset Tokenization, where tokens represent legally issued instruments and not abstract digital units. For platform builders, this removes the need for post-issuance remediation caused by incorrect onboarding or allocation errors.
2. Investor Onboarding and Identity Enforcement
Investor onboarding is tightly coupled with token behavior in ERC-3643-based systems. Wallets are associated with verified identities that reflect KYC status, investor classification, and jurisdiction. This identity layer becomes the gatekeeper for ownership and transfers, ensuring tokens circulate only among approved participants.
In RWA tokenization platforms that are issuing ERC-3643 RWA Tokens, this structure supports individual investors, institutions, and custodians under a single framework. Builders gain a consistent identity model that stays enforceable across primary issuance and secondary markets.
3. Transfer Logic Designed for Regulated Markets
Secondary transfers are where many RWA platforms fail. ERC-3643 addresses this by enforcing compliance checks at every transfer execution. Buyer eligibility, seller status, and jurisdiction compatibility are validated before settlement. This removes dependency on manual approvals or centralized operators for routine transactions.
This allows compliant peer-to-peer transfers in RWA platforms while maintaining regulatory integrity. The result is controlled liquidity that mirrors how regulated assets trade off-chain, without breaking compliance when tokens move between holders.
4. Embedded KYC and AML Enforcement
Regulatory obligations do not end after onboarding. ERC-3643 supports continuous enforcement of compliance obligations through identity-linked controls and rule evaluation. This makes ERC-3643 KYC AML Tokenization practical at scale, since changes in investor status can immediately affect token permissions.
If an investor loses eligibility, transfers can be restricted without freezing the entire system. For RWA platforms, this enables real-time compliance enforcement while maintaining operational continuity and avoiding disruptive contract migrations.
5. Lifecycle Management and Ongoing Supervision
Real-world assets require ongoing oversight after issuance. ERC-3643 includes administrative controls that support corporate actions, regulatory intervention, and asset lifecycle events. Issuers can execute freezes, forced transfers, redemptions, or recovery actions when required by law.
This is critical in production-grade asset tokenization platforms, where assets remain subject to courts, regulators, and contractual obligations. Builders gain a framework that supports long-term operation, audits, and regulatory interaction without redesigning the token layer.
Launch compliance-driven RWA platforms using ERC-3643
ERC-3643 Implementation Checklist for Issuers & Platforms
Implementing ERC-3643 in a production RWA platform requires coordination between legal structuring, technical design, and operational controls. The checklist below outlines the important steps that need to be followed by RWA tokenization platform development teams to move from concept to compliant deployment, with a focus on long-term operability and regulatory alignment.
- Define the legal asset structure first: Confirm how the underlying asset is issued, held, and transferred under applicable laws before mapping it on-chain.
- Engage jurisdiction-specific expertise: Work with a partner that offers RWA legal consulting services to define investor eligibility, transfer restrictions, and reporting obligations.
- Design the identity and onboarding flow: Map KYC status, investor classification, and jurisdiction to wallet identities used by the platform.
- Configure ERC-3643 compliance rules: Encode issuance and transfer conditions directly into the compliance engine before token deployment.
- Plan custody and ownership representation: Decide how self-custody, institutional custody, and nominee structures will interact with token ownership.
- Prepare for secondary market controls: Ensure transfers between investors remain compliant across trading venues and jurisdictions.
- Align asset type with platform architecture: Apply these steps specifically to real estate tokenization development, where ownership, cash flows, and regulatory oversight persist long term.
Bottom Line: Why ERC-3643 Is the Future of Regulated RWAs
RWA tokenization platforms succeed or fail based on how well on-chain behavior matches real-world rules. When identity, transfer limits, and supervisory actions sit outside the token layer, every edge case becomes a workaround. Over time, this leads to fragile systems that are difficult to scale, audit, or adapt to regulatory change.
The ERC-3643 Token addresses this by treating compliance as part of token execution. Identity checks, transfer permissions, and control actions occur at the same layer as balance updates. This keeps asset behavior consistent as tokens move across wallets, venues, and jurisdictions.
For platform builders, ERC-3643 offers a stable base for long-term operation. It reduces custom glue logic, limits migrations, and supports regulated asset flows without redesigning the core token architecture as requirements continue to change.
Build a Compliant RWA Tokenization Platform with Shamla Tech
Shamla Tech is an RWA tokenization development company building compliant platforms using the ERC-3643 token standard. Our architectures enforce identity verification, transfer restrictions, and supervisory controls directly at the smart contract and protocol layers.
We build end-to-end RWA tokenization platforms covering issuance workflows, investor onboarding, compliant secondary transfers, and long-term asset supervision. Our systems are designed to operate within regulated environments without relying on off-chain enforcement or manual controls.